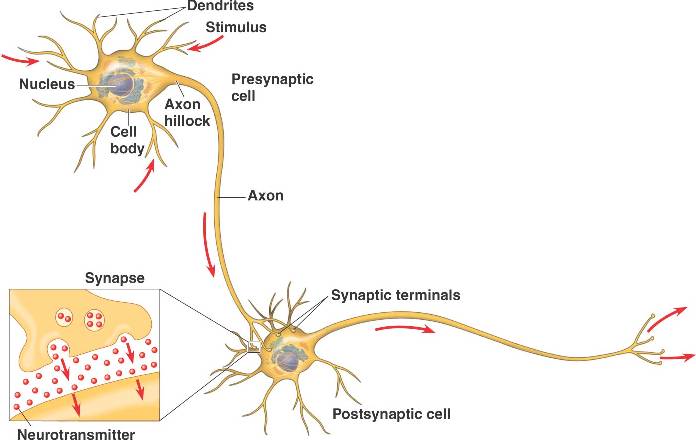
What do you think about when you day-dream? I mean really day dream. Those moments where you are
What do you think about when you day-dream? I mean really day dream. Those moments where you arereally deep into your own little world. Those moments where for a few brief minutes you forget about appointments, parking tickets, homework, reports, car payments, taxes, global warming, job security, the economy, the tea party; those moments where you just drift into existential bliss and tune out the societal noise.
What do you think about? Maybe you think about yourself and ask what makes you you? Why am I here, why are we all here? In those moments, however do you ever wonder or just sit in awe of the 3 pound organ in your head that allows you to tune out the noise and ask such deep questions? Do you ever wonder how the human brain works?
 As crazy as it sounds, this is still the central question of neuroscience today. Which, may appear to be surprising to some, seeing as it is one of the most well funded disciplines in all of biology. However, you really have to take into account the enormous mind-boggling (no pun intended) complexity of the human brain! It is made up of millions of individual neurons all connected with one another by TRILLIONS, yes that's right, trillions of synapses (the small gaps between two interacting neurons). We have known since the 1950's how individual neurons initiate signals and send them to another neuron. We also have a pretty good idea how the brain performs simple motor tasks such as grabbing a pencil or interpreting sensory information such as someone poking you with said pencil, known as neural circuits. Where it gets really messy and complicated is when we start to investigate things such as decisions making, problem solving, and the big one consciousness. How would we even begin to start doing this?
As crazy as it sounds, this is still the central question of neuroscience today. Which, may appear to be surprising to some, seeing as it is one of the most well funded disciplines in all of biology. However, you really have to take into account the enormous mind-boggling (no pun intended) complexity of the human brain! It is made up of millions of individual neurons all connected with one another by TRILLIONS, yes that's right, trillions of synapses (the small gaps between two interacting neurons). We have known since the 1950's how individual neurons initiate signals and send them to another neuron. We also have a pretty good idea how the brain performs simple motor tasks such as grabbing a pencil or interpreting sensory information such as someone poking you with said pencil, known as neural circuits. Where it gets really messy and complicated is when we start to investigate things such as decisions making, problem solving, and the big one consciousness. How would we even begin to start doing this?
Well whenever scientists try to investigate something that is to complicated to observe in the field or in a lab setting, we try the next best thing we develop computer simulations, or mathematical models, to create the closest thing we can to reality inside a computer. This has been done for years, in fact one of the pioneers of computer science Alan Turing goal was to ''build the brain'' and ended up building a computer. As you might have guessed the mathematics must be extremely complicated in order to program a simulation of a human brain, and you are right! Enter the crazy, complicated field of computational neuroscience.
Even though the idea to simulate the brain using computers has been around for almost 60 years, what has just become available is the computational power to actually perform such tasks. First, though I just want to briefly give a crash course in how to approach modeling.
 There is a trade-off when developing mathematical models or computer simulations, because you want to make it as realistic as possible, otherwise your results could be shaken off as unrealistic. However, the more variables and dimensions you add to a model, the more complicated the mathematics gets, i.e. the more moving parts there, are and the greater the chance something could go wrong. My graduate adviser goes by the rule that a great model will follow the 80-20 rule, meaning that you cannot account for 100% of the things going on in a system, so you only want to account for 20% of the most important variables.
There is a trade-off when developing mathematical models or computer simulations, because you want to make it as realistic as possible, otherwise your results could be shaken off as unrealistic. However, the more variables and dimensions you add to a model, the more complicated the mathematics gets, i.e. the more moving parts there, are and the greater the chance something could go wrong. My graduate adviser goes by the rule that a great model will follow the 80-20 rule, meaning that you cannot account for 100% of the things going on in a system, so you only want to account for 20% of the most important variables.And this is where neurosciences have struggled, because as I said before, the human brain is IMMENSELY complicated. Some scientists believe that simulations must also account for the genes being expressed in each neuron as well as individual ion channels in each of the millions of individual neurons on top of the trillions of precise connections. Brain hurt so far? Don't worry so does mine, but stick with me here! What really is going to impress you though is that recently computational power has reached the point in which we can actually do this!
 |
| This is heavy stuff, here's probably what your brain is feeling |
 Not all computational models have the detailed approach as Blue Brain. Researchers at the University of Waterloo in 2012 developed a brain model called Spaun which simulates a much smaller scale than Blue Brain, still 2.5 million neurons. The most interesting thing about this simulation is that it was designed to perform cognitive tasks, while others like blue brain simulate more of the actual physiological connections of an entire brain. Spaun has the ability to do simple tasks such as look at a set of numbers, remember, and then repeat the numbers back by writing them on a piece of paper, and other tasks similar to ones on basic intelligence tests. Pretty cool eh? The big breakthrough, and in my opinion the most intriguing finding, was Spaun's limitations.
Not all computational models have the detailed approach as Blue Brain. Researchers at the University of Waterloo in 2012 developed a brain model called Spaun which simulates a much smaller scale than Blue Brain, still 2.5 million neurons. The most interesting thing about this simulation is that it was designed to perform cognitive tasks, while others like blue brain simulate more of the actual physiological connections of an entire brain. Spaun has the ability to do simple tasks such as look at a set of numbers, remember, and then repeat the numbers back by writing them on a piece of paper, and other tasks similar to ones on basic intelligence tests. Pretty cool eh? The big breakthrough, and in my opinion the most intriguing finding, was Spaun's limitations.Unlike most computers that just evaluate millions of possible decisions in milliseconds and then finding the best answer (think chess playing supercomputers), Spaun instead paused; it hesitated before giving an answer! It actually thought! To me that sparks a certain sense of fear that one day simulations like this may become self aware and destroy all of mankind! It also sparks some extreme interest and hope that these models become increasingly more accurate.
And I have no doubt that
they certainly will! It is just going to require a lot more knowledge of neural
connectivity in the brain, as well as you guessed it more computational power.
Which ultimately is the limiting factor, as always, when it comes to really
complicated models such as these. One day however, I have no doubt that
we will have cell phones with human-like AI like operating systems, similar to
one in the recent Spike Jonze's movie Her, hopefully minus the awkward dating
your phone phenomena. All AI thoughts and/or concerns aside, realistic
computer simulation of the human brain will contribute greatly to understand
how exactly the human mind works as a whole, as well as, aid in solving
diseases in which our minds' machinery goes haywire; such as Alzheimer's, depression,
and even schizophrenia. As well as aiding in understanding how we can perform
abstract processes such as what problem solving, creativity, and create/store
memories. Most importantly however, these models could very well hold the key
to understanding the process that gives our species the ability to ponder its
own existence. So keep at it computational neuroscientists! Math/computer/biology nerds are rooting for
you!
A
heavy blog like this requires some heavy music! Enjoy some mind bending music the next time you ponder your own existence!
References
1.) Eliasmith, C. and O. Trujillo. 2014. The use and abuse of large-scale brain models.Current Opinion of Neurobiology 25:1-6.
2.) Eliasmith, C., T.C. Stewart, X. Choo, T. Bekolay, T. DeWolf, Y. Tang, and D. Rasmussen. 2012. A large-scale model of the functioning brain. Science 338:1202-1205.
3.) Markram, H. 2006. The blue brain project. Nature Reviews: Neuroscience 7:153-160
4.) Stewart, T.C., F.X. Choo, C. Eliasmith. Spaun: a percption-cognition-action model using spiking neurons
http://www.gizmag.com/brain-computer-simulation/25349/
http://phenomena.nationalgeographic.com/2013/02/14/will-we-ever-simulate-the-brain/
Images
http://www.titaniumteddybear.net/wp-content/uploads/2010/09/lolwut-jurassic-face-thread.jpg
http://www.quickmeme.com/img/1c/1cba02b056944308e72401de0acbf9dbb471aad66deea493613a633be13ab92d.jpg
http://www.troll.me/images/ancient-aliens-guy/computers-how-do-they-work-thumb.jpg
http://www.artificialbrains.com/images/blue-brain-project/blue-gene-p-architecture.png
http://images.scholarpedia.org/w/images/8/86/Encyclopedia_of_computational_neuroscience.gif